Erhalten Sie Zugang zu diesem und mehr als 300000 Büchern ab EUR 5,99 monatlich.
- Herausgeber: Books on Demand
- Kategorie: Ratgeber
- Sprache: Englisch
Many of you have asked for a simplified version of the book LE COACHING SDHEA, a manual of 636 pages in French*, almost unsuitable for newcomers, but biblical for all professionals, doctors or psychologists, for reflexologists, naturopaths, psychiatrists, from the medical world and the medical world, and the systemic technical therapies included in the book allow you to: to train a professional in a very short time, from a few hours to a few weeks. But that is not the purpose of this book, but rather to allow you to re-read the book from a new angle that concerns you and that is only just beginning. The reader will not look for solutions to his personal case (stress, disorders due to disaster situations, demoralization, suicidal thoughts or various apathies, loss of a loved one ...), but he will find them when reading this book. He will then find the solution to his problem on his own, almost without realizing it. You already have free access to MP3 tools on the site that can help you reduce or eliminate stress. https://www.successcoach.fr/la-relaxation-sdhea Usable tools such as emotion management, dietetics or sports, memory control, NLP, Eriksonian hypnosis, relaxation or sophrology in a systemic way allow you to respond to the problems of the moment. The book is published in six languages.
Sie lesen das E-Book in den Legimi-Apps auf:
Seitenzahl: 321
Veröffentlichungsjahr: 2023
Das E-Book (TTS) können Sie hören im Abo „Legimi Premium” in Legimi-Apps auf:
Ähnliche
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION
VOLUME 1
CHAPTER I HUMAN AND HEALTH SYSTEMS ANALYSIS
CHAPTER II EMOTIONS AND EMOTIONAL BALANCE:
CHAPTER III EXCELLENCE OF BODY AND MIND:
EXERCICES
VOLUME 2
CHAPTER I: SYNCHRONIZATION
EXERCICES
VOLUME 3
CHAPTER I: TRANCE
CHAPTER II: TRANCE WORK PROPER: ABSORPTION – CONFUSION – RATIFICATION – SIGNALING – REASSOCIATION
CHAPTER III: HYPNOTIC SUGGESTIONS THE METHOD OF EMILE COUÉ
CHAPTER IV: REASSOCIATION - EXIT FROM TRANCE
CHAPTER V: PRACTICAL TECHNIQUES OF INDUCTION
EXERCICES
VOLUME 4
RELAXATION: DEFINITION
EXERCICES
VOLUME 5
SOPHROLOGY
PLEXUS CHAKRAS AND COLORS CHART
VOLUME 6
NEURO-LINGUISTIC PROGRAMMING
EXERCICES
INTRODUCTION
COACHING SDHEA for beginners allows everyone to know everything about the functioning of oneself and others thanks to the analysis of human systems, the management of emotions, the excellence of health through dietetics, sport, tantra and memory, but also therapeutic speech, NLP, hypnosis, relaxation and sophrology.
You'll know enough to take control of your life and get better instantly.
To deepen your knowledge of COACHING SDHEA and change your profession, to set up as a freelancer in the field of health, it is better to approach this study with the 636-page bible "COACHING SDHEA" on sale on Amazon.com free of charge and without delay.
VOLUME 1
HUMAN SYSTEMS ANALYSIS
HEALTH AND EMOTION MANAGEMENT
EXCELLENCE OF BODY AND MIND
CHAPTER I HUMAN AND HEALTH SYSTEMS ANALYSIS
What is the definition of coaching?
The term coaching contains the idea of a gradual shift from an initial situation that is balanced, but no longer wanted, to another final situation, which is desired.
For example, you smoke, you're fine, but you want to quit for some reason. Coaching accompanies you to quit smoking, that's all (and above all not to smoke again!)
And COACHING SDHEA then, why SDHEA?
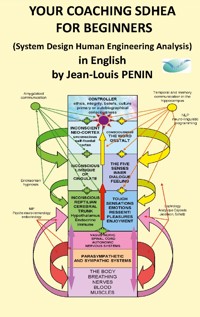
It's the same as coaching but the approach is different. We're going to use the analysis of the initial situation in terms of the system, we're going to do what's called systems analysis. That means System Design Human Engineering Analysis.
Are there any rules to follow in COACHING SDHEA?
Yes, the first rule is that if there is no request from someone (who is called the coachee), you cannot forcibly coach them.
The second rule is that you should not look for a solution towards the balanced final situation (we also say homeostatic, it looks better!). This is called "the therapist's low position" because he says he doesn't know anything (but I'd say everything!)
Do we think you are capable of doing something?
This is called efficiency, which is the belief in yourself that you can do something. First of all, you have to start by believing in yourself that you are capable of modifying the coachee's situation, but above all not of finding the solution, it is he who will find it, not you, and for this he will have to choose (or we choose for him if it is easier) among the techniques proposed, those that will lead him straight to the goal.
And as the comic Pierre DAC used to say, "Can he do it? Yes, he can do it...!! »
What are the first tools of coaching?
There is rephrasing. It is the practice of listening to the person by rephrasing what you hear.
Example: the person tells you: "I should lose weight", you answer, "so you should lose weight" and he continues by saying "yes, but I don't know how to go about it, you go on to say, "if I understand correctly you don't know how to go about it?"
When you are faced with a request, tell yourself that the solution is not far from the request, but do not look for it.
What is the difference between coaching and COACHING SDHEA?
The difference is that COACHING SDHEA is allrounder. Here is an example from the experience of a COACHING SDHEA session:
One day, a person came to a consultation asking to change his beliefs that he had acquired in a manifest distrust of anyone with whom he wanted to associate. She had this need to succeed in her professional life. This person was covered in patches of eczema all over his body and his request was not about this obvious physical condition because he did not know that Therapeutic Coaching could treat this kind of condition. The success of his request depended on the realization of his long-standing relationship with his brother who had been dead for several years and with whom he was very emotionally connected. His patches of eczema, which are a form of communication "on the edge" of the skin, disappeared along with the solution of his regained healthy belief. This is the path of eczema care that has been followed and treated by Eriksonian hypnosis.
What is the Coach SDHEA's approach?
It is a therapeutic approach in the broadest sense.
Therapeutics is derived from the ancient Greek noun therapeutikê which means "the art of caring for someone".
Caring for someone doesn't mean that someone is sick. In the word 'psychotherapist' or in the word 'therapy', the term therapeutic is not necessarily associated with the treatment of an illness, which in France, as in many countries, is reserved exclusively for doctors.
What matters most in COACHING SDHEA is the evolution, the movement, from one situation in equilibrium to another desired situation in equilibrium as well. The Coach SDHEA therefore considers that the health of his client is good but not good enough and that we can do better.
What tools does the Coach SDHEA use?
The Coach SDHEA will use tools to make this change or evolution a success.
The tools we will use are Systems Analysis, Emotion Management, Therapeutic Speech, the famous terpnos logos, Eriksonian hypnosis, relaxation, sophrology, and NLP. All these techniques will be developed to allow the transition from one state to another and to do COACHING SDHEA.
What is Systems Analysis?
Systems analysis is an approach of the mind that considers the human person in his environment as a system.
To be able to do systems analysis, you must be in front of a system. To do this, you must learn to recognize what a system is.
So how do you recognize a system?
First, it is the individual as such who is a system, and we will see why later.
But there are other systems, such as the group, the family, the work group, and many other environments that form a system or systems.
A system is recognized when it is possible to determine four factors that make it up.
These four factors are elements, interactions (between elements), an objective or goal to be achieved (which is followed by the interacting elements), and finally a control (which checks that everything is going well to its objective and not beside it).
Can we have concrete examples?
Yes, for example:
These are people or living beings like you and me and the Coach SDHEA, the spouse, the parents, the children, the dog, the cat, the medical or paramedical, hospital, surgical staff, objects that have a meaning such as gifts received or given, substances or products such as medicines, food (vitamins, trace elements), food, etc. Drugs, compulsive products such as chocolate, fats, sugars, in fact all the material elements with which we are likely to have an interaction that we will see now.
Examples of interactions include:
These are the emotional relationships with the living environment, the environment with which we are in a relationship in each context, but also all the words exchanged between people, and mainly those that involve the Coach SDHEA and his coachee.
So, what is the objective?
It can be an altered state of health, physical or mental abilities, behaviour’s, self-confidence, energy, calmness, focus, performance, resources, and so on. Be aware that to form a system, you need and only need one objective, because if you have two, there must be two systems.
I'll give you an example. I come to see the Coach SDHEA because I eat too much chocolate and have allergies to cat hair. Well, that's two systems to analyse. We'll see how later.
So, what is the purpose of control?
Let's take an example to see how a control maintains an objective: that of eating too much chocolate.
As simple as it sounds, in the example above like eating too much chocolate, it's an answer to the question how do you know you're eating too much? It's not so simple to see but simple to understand. The best proof that you get control of this problem is by making the person eat even more chocolate as a kind of punishment, and then he picks up, takes control of himself, and goes back to eating chocolate normally. For example, it will be said that it is her sister who tells her all the time that she eats too much chocolate, that's how she knows it, but this is only an indication, it can also be hives or temporary sickness, or discomfort due to chocolate bulimia. But if you look a little, you will find that it is a search for pleasure that compensates for a lack of affection that maintains bulimia and you will then have to remove this control to give it back to your prefrontal cortex or frontal lobe.
So, control is anything that keeps a goal in a state of equilibrium, even if it is not wanted. Think, for example, of the request “I don’t want to smoke anymore or I want to quit smoking", but also there is "I have suicidal thoughts" So what to do with such controls that maintain such goals?
So, what is the purpose of the systems analysis process for the Coach SDHEA in fact?
The system analysis approach allows the Coach SDHEA to obtain a new homeostatic balance for the Coachee, a balance that responds to his conscious or unconscious request. If there are several objectives or sub-objectives nested within each other, there will be as many corresponding systems as possible or subsystems. Each system has its own objective and its control to achieve it, or to keep it in balance or homeostasis.
But let's go back to efficiency: How does it work?
Efficiency is the Coachee's belief in the ability of the Coach SDHEA to change his state to the one he desires. With systems analysis, we can already see better what system he is in and where he wants to go, even if we don't yet know how to support him. But that's still enough.
This is where the personal development of the coach plays a role because it allows the "active listening" interaction that is essential to the efficiency system.
In conclusion, remember that all the tools contained in this book will serve no purpose other than to reinforce your belief and obtain efficiency. The coachee or the person with whom you are in a relationship will feel this and will make their systems work to modify them, and you will not have to do anything, not even look for a solution, they will find it. Here's how it works. The coachee grows in you and this changes their abilities and behaviours.
What is a system structure?
The human system is a system made up of a very large number of elements, interactions, objectives, and controls, which are themselves systems made up of multiple subsystems. The human or coachee system arrives in consultation in an apparent balanced state called homeostatic.
This system, of which all the parties that have reached this point all had positive intentions in the first place, have done their job well and the control is over. This position of a system whose control has finished its work and is in the off or closed position is called STRUCTURE.
Can you give us an example of successful change through systems analysis?
A person comes with stress from noise caused by their next-door neighbors that they can no longer stand. The change of system can consist of:
1. Modifying Elements:
He moves or eliminates all his noisy neighbors, that's the heavy fix.
2. Modifying interactions :
He insulates his apartment or goes to buy earplugs, which is sometimes enough.
3. Modification of one's control to noise (perception of annoying noise coming from an excess of cortisol in one's endocrine system (relaxation) or modification of auditory sensitivity by modification of the corresponding sub modalities with NLP, this is the COACHING SDHEA solution
Modification of its purpose:
Managing one's bad stress through breathing and deep relaxation, the goal of neighbors' noise becomes secondary.
5. Changing control by cropping. He associates the noise with the virtual presence of his grandmother, whom he loved very much and who came to set up on the landing with her neighbours (reframing with NLP).
This is a concrete example, and it is the coachee who chooses his solution, often the last one and alone and with a lot of emotions.
What is Coach SDHEA Personal Development?
Personal development is a set of psycho-sociological benchmarks necessary to acquire a satisfactory level of efficiency.
The Coach SDHEA will have to master his own emotional system, increase his belief in his efficiency, raise his moral values and integrity, as well as his ethics in the course of his work. It will even have to increase its level of excellence, as will be seen below. He must be always unconditionally positive and is trained to achieve this permanent state of mind. He then accesses all the other effective techniques such as active listening and thus continues to develop his unconscious.
Finally, the Coach SDHEA must believe in all the positive intentions of his client and communicate them to him.
Here's an example: If a candidate shows up 50 kg overweight, and he's obese, you start by congratulating him on all the work he's had to put up with to get to this point, that's an achievement. On the other hand, he doesn't want it anymore, he aspires to a different kind of success, and then you must start by listening to him without any preconceptions.
How can we elevate our moral values and integrity?
Integrity is an intrinsic quality that allows you to intervene on your client unconsciously. All the solutions that are useful to your customer are in them and not in you. By being honest, you access all your unconscious parts and make them your allies to obtain one or more solutions.
How can you be unconditionally positive?
It is a state in which you must be constantly to allow you to progress in COACHING SDHEA. It is an application of the middle way, a kind of TAO of existence. In any seemingly negative situation, there is always a positive element that is at the source. Practice looking for the positive in any situation unconditionally. Only this attitude allows you to discover solutions to the problems that are submitted to you. You need to be the catalyst or witness to the solution.
It's about getting a positive mindset with no strings attached to reality, no matter how apparent the conditions of reality are. Here are the reasons for such a state of mind:
(1) The whole system does its job to the best of its ability. It is in this sense that all issues should be considered positive.
2° By behaving in a positive way with your customer, you are already changing the perception of his problem.
3° Your effectiveness is increased tenfold if you consider your client's problem in an unconditionally positive way.
Note: This is not to consider what is happening to your customer to be positive; It's about having a habitual mindset that is unconditionally positive.
What is Middle Way Theory?
Work on this paradox: "Truth contains the
lie" TRUE or FALSE? or some other paradox: The
Does a lie contain the truth TRUE or FALSE?
With unconditionally positive rephrasing, you have learned that in an appreciation of a negative situation, there is always something positive. Middle reformulation is a form of reformulation that consists of associating the negative and positive parts of a situation:
Think and don't think about the number 6...
Don't think of a pink elephant, or think about it, or another colour or not...
To have a lot of money or not a lot of money
Dive infinitely slowly or not in this pool filled with hot or warm water or at a temperature that suits you.
Example of middle rephrasing:
When you rephrase what you are told, do it through the middle: To do this you add the opposite of the situation with formulas from the simplest to the most sophisticated such as: ... or not (you get it... or not...?) ... at certain times, and not at other times... Maybe yes, maybe no... ... Sometimes yes, sometimes not... So, it is true or false to say that.... You rephrase: "I would like to lose weight" to "So, you would sometimes want to lose weight and sometimes you don't..."? Or "I'm unwell..." In "yes, you have discomforts it's good and also well-being it's bad..." »
If I say to you, "You are the smartest person I know or don't know,” the content of my rephrasing will unload the emotional charge of the judgment I might have on you in the context of a value or belief that has control over that information that comes to you. Under these conditions, the effect is neutral and has no effect on the conscious plane. On the other hand, it is not a sentence that is meaningless for the unconscious, which will have perfectly understood the content of my sentence which speaks of your intelligence.
How to practice active listening to your coachee?
Assume that the whole solution lies primarily in the Coachee and not in you. Under these conditions, the first job is to actively listen to your customer and clear the possible solutions that would come to mind. Rest assured, none of them are the right ones. The only solution will emerge from your customer as soon as they are listened to and hear what they are saying from your listening. This is active listening.
What are beliefs and values for the Coach SDHEA?
The set of beliefs forms the supreme foundation of the possible or the impossible. In computer metaphor, these would be the source programs that are almost common to each of them, allowing all other personal programs to work. An Example with Identity Belief
It means that I accept who I am (age, physical), I have value, I am respected, I love and respect myself, I deserve what I am, I have a field of possibilities to be, I achieve my mission and so on. By re-establishing one of these identity beliefs, you gain access to the establishment of values.
Values should be ranked to better understand one's own functioning before listening to the other's functioning.
Examples: success, respect, power, safety, conformity, tradition, kindness and many more.
The values allow the brain filters and the sorting of the elements and interactions of the Coach allowing him to access his objectives. It is a question of having a different image of Coach SDHEA (modelling) or of value, for example, respecting the rules of morality and correction such as the rules of ethics and deontology of the SDHEA FUND association.
Here are some examples of beliefs and values that are useful for your personal development.
Some examples of COACHING SDHEA sessions?
1° Example: A person comes with a headache that has persisted for 20 years. The Coach SDHEA "It's great! You've had to hold on to it for a long time."
2nd example: Your coachee: "I smoke too much". (And no, I would like to quit smoking, which is a positive formulation for the patient) Coach SDHEA's Response: "Do you smoke too much?" The patient "yes, I smoke too much, I'm fed up... The Coach SDHEA: "Well, that's something you're doing really well" The Patient: "What am I doing?" The Coach SDHEA "Smoking too much... since you're very good at maintaining that... until now”.
3rd example: "I came to see you because I want to lose 20 kg" Coach SDHEA's answer "What are you going to do with all this lightness that you are going to gain?"
4° Example: "I don't have confidence in myself and..." Coach SDHEA: "It's completely normal, it's because.
If you don't know yourself well enough, then you Don't trust yourself.
Would you like to gain from being known by you? »
CHAPTER II EMOTIONS AND EMOTIONAL BALANCE:
What is the purpose of emotions?
Emotions are factors in the evolution of human beings and a means of communication-action (to make people do or to make them act).
Who handles emotions in the brain?
This is the limbic hypothalamic system or SHTL for short (in French Système HypoThalamo Limbique).
This development allows a diversification of emotions from the 5 senses and no longer only from the olfactory as at the beginning thanks to the limbic system and the hypothalamus. Indeed, emotions are managed by the limbic system via the amygdala which directly controls the nervous and endocrine systems (via the pituitary gland)
What is the emotional system?
The emotional system contains four basic emotions: Fear: Feelings of anguish, shame, surprise, guilt, remorse, fear, phobias, humiliation, contempt, dismay, terror, avoidance, submission, disgust, embarrassment, annoyance, worry, nervousness, panic, terror. Anger: Feelings of discontent, resentment, self-accusation, indignation, resentment, exasperation, fury, hatred, violence, aggressiveness, protest, and animosity.
Sadness: sorrow, regret, frustration, injustice, melancholy, gloom, nostalgia, depression, resentment, despair, self-pity, tears, departure, separation.
Joy, Amusement, and Interest: Contentment, admiration, interest, eroticism, amusement, wish, pride, joy, tenderness, expectation, need, thrill, euphoria, ecstasy, pleasure.
NOTE: If you are convinced that there are other emotions than the 4 primaries above, remember that the main thing is in the optimization of the effectiveness of the Coach SDHEA (effective-not effective) and not in the true-false axis of the reality that is not well known.
How does the emotional system work?
The emotional system is originally a means of communication to act or to evolve or to make people act. Repression, maladaptation, or lack of movement because of an emotion creates a vicious circle that spirals out of control. Feelings are real stored emotions that alter people's emotional lives.
What about movements provoked by an emotion?
This is the principle of Gestalt, which is a therapy developed around 1950 by Perls Fritz and his team. The theory is that if emotions have been stored by the Coachee in the form of feelings because of blocking the associated natural movement, there is a good chance that their goals are not far from these storages. Emotions play a natural role in social communication and are the source of movement in each context. If you change the context or the movement, you change the type of emotions or their intensity. In a way, therefore, it is a question of making a difference in the context of an interaction. Imagine movements for anger and love, for example.
But can movement create emotion?
Absolutely, and this I have called Imotions as emotions can be expressed by outward movement, so it is possible to use Imotions for inward movements. Movement creates an emotion.
An emotion must start from a significant mental state to one or more movements that allow communication with others. When in a context there is one or more movements usually used to express an emotion, you can create an imotion, i.e., an incoming inverted emotion. If the copied emotion also exists in the form of a feeling (stored emotion), it is very likely that a reaction will take place allowing the total or partial destocking of this emotion. The person then recovers a feeling of liberation and a new psychic energy, which is no longer used to maintain the storage of this emotion. This is the simplified principle of Gestalt.
And how do you stop feeling emotions?
Movements can be created virtually by kinesthetics re-enactment in an imaginary "as if" for the same results. The process is said to be associated or the person is said to be associated, the opposite being dissociated. As a result, a person who dissociates himself from his kinesthetics’, even if he is constructed by thought, can no longer feel emotions, let alone release old emotions.
And what are impulses?
The reptilian brain, or brainstem, has been closely linked to the fundamental impulses of human beings for millions of years. A distinction is made between life drives (hunger, thirst, contact, avoidance), evolutionary drives (aggressiveness), sexual drives (attractions, pleasure), interest drives (social, games), but also the absence of drives (satiety, withdrawal, death drive)
The progressive development of the reptilian brain has allowed the establishment of a border called limbic allowing two fundamental new elements:
1) Short-term storage of frequent or habitual impulse states through the amygdala
2) The hippocampus' long-term memory of contexts that give meaning to the work of the amygdala. It is the conjunction of the work of the impulses and the storage of the amygdala and hippocampus that allows the hypothalamus to trigger the movements of the emotional system.
Are there any other basic emotions?
There are four basic emotions that are related to hormonal systems and to basic movements and drives. All other quasi-emotions (shame, pride, embarrassment, pride, shyness, guilt, jealousy, surprise, disgust) are mixtures of emotions or emotions refined by the neocortex or constructed feelings or feelings. For example, a mother's attachment to her child is a late construction of the neocortex and not an emotion of the limbic system, much less an impulse of the primitive reptilian brain. A distinction is made between the association of basic emotions and the storage of associated emotions.
Storage of emotions and drives, the appearance of context as energy storage.
The storage of emotions should not be confused with the storage of impulses. This storage of impulses is an unconscious memorization. It is normal and is the result of human evolution since the beginning of humanity on earth. When there is no movement with emotional energy, this energy is stored as context by the hippocampus (contextual energy)
What is temperament and mood?
Temperament is the permanent maintenance of one of the basic emotions by the combined work of the neocortex and the limbic system. This causes the same endocrine effects as the emotion itself, as well as a quasi-storage effect of emotions or feelings. These then become the equivalent of a cellular movement of the body, which is called feeling, which is the basis of the body's behaviour. Mood is the natural tendency of the above temperament, but in the short term and not permanently (good or bad mood, mood swings...).
How do you control your emotions?
The mere awareness of the emotional system by the neocortex allows the control of the emotional process, i.e., its control.
The implementation of a controlled 4-step breathing allows emotional control (see below for the definition).
External therapeutic treatment can change the system, especially if it is out of whack. It can be the direct work on the emotional system, the work on the unconscious control carried out in an Eriksonian trance, the work on the awareness of the body through analytical sophrology or relaxation. Finally, the work between drives, emotions, and feelings on the one hand, and the contexts memorized by the hippocampus on the other hand, can be carried out by NLP.
What are the movements that control emotions?
There are 7 possible actions to control emotions:
1° Body positions and movements induce emotions if they are stored beforehand (feelings and feelings).
2° The coachee's active reflexive listening allows him to become aware of his feelings and feel and induces a control of parasitic emotions (putting the pains into words).
3° The change of context of an emotional memory modifies or releases a storage of emotions.
4° The implementation of a positive behavior (emotions "love") most of the time abolishes all other behaviors (one emotion drives out the other).
5° Relaxation allows you to cut off the movements and the return to the destocking of emotions but does not destock. You must take control through controlled breathing or controlled body movements to be able to control and destock.
6° When a person cannot express an emotion with his or her body (contextual prohibition), another emotion can be expressed to use the unused energy. 7° The internal or external dissociation of consciousness and kinesthetics cancels out the feeling of the emotional system.
CHAPTER III EXCELLENCE OF BODY AND MIND:
The excellence of the coach will focus on 4 parts:
The first is based on the dietetics of the body and brain.
The second is based on sport, the glorification of movement, work on the four pillars of sport and the theory of beauty, plasticity, and health.
The third on Tantra, therapeutic touch as a path to well-being
The fourth, on natural memory and cerebral sport or artificial memory.
A – EXCELLENCE THROUGH DIETETICS:
How to practice body and brain dietetics?
To practice dietetics, you must respect a few basic rules, otherwise it's like a garden with scattered weeds, it's less beautiful... but hey! We're going to use some essential rules to keep things simple.
Faced with the overwhelming amount of information on what to do or not to do in terms of weight, diet, normal or vegan or organic nutrition or adapted to a persistent belief, it is necessary to go back to the basics to obtain a convincing result.
What are the essential nutrients?
Regardless of your body index (excess or deficit compared to the average norm), it is necessary to first provide the body, vital organs, viscera, and brain with the minimum daily nutrients, otherwise the whole edifice of the newly acquired nutritional system will disappear sooner or later, this is commonly referred to as the "yo-yo effect". What you have achieved in terms of weight so far is your equilibrium weight, even if it is changing more or less quickly. It may not be the ideal weight of excellence that you would need, but it is the one that you managed to achieve during your lifetime. So, in terms of systemic balance, it's the right weight, even if it's excessive, this point needs to be well understood in order to be able to apply the desired changes. To change your weight (both downwards and upwards), you must first make sure that you provide your body with all the nutrients you need for your entire body, including your brain. So, you forget about diet-based methods.
You need enough protein Count from your ideal weight that you want to achieve, otherwise you will make calculations about your current wrong weight. For example, if you are 1.70m tall, your ideal weight is 63 kg (male or female by the way, it doesn't matter at this stage). Main proteins: rice – milk – soya). Depending on your activity, you need a daily protein intake of 1 to 2 grams of protein per kg of weight, i.e. here in the example between 63 gr and 126 gr of protein per day, which makes about 20 gr to 40 g of protein per meal spread over 3 meals a day (i.e. about 100 to 200 gr of meat, fish or cheese). Lipids. You will take care to promote as much as possible vegetable fatty products rich in omega 3 and omega 6 (2 g of omega 3 and 10 g of omega 6 per day for a man, respectively 1.6 g of omega 3 and 8 g of omega 6 per day for a woman. (Source: WHO - Rapeseed oil and grapeseed oil are recommended). Banish all other fats except for moments of shared or solitary pleasures that you can reserve for yourself once a week for example (1 to 2 tablespoons per meal).
What is the principle of protein glasses?
This way of looking at food by the protein absorbed will not focus you on high or low calories because this technique is much more depriving and traumatic for the brain. You will then adapt your diet according to the proteins absorbed without considering the correspondence with calories, i.e., without considering the cooking method used. This is because it modifies the calories absorbed but not the quantities of protein needed. That is what is new about this approach. Your glasses are not calorie glasses but protein glasses, which is very different. In fact, most so-called "low-calorie" diets cause you to reduce your quantities by starving you and change your favourite nonfat cooking methods outside of your favourite tastes, which leads to food disaster that leads to failure. As soon as you eliminate from your diet a large part of all the other fats derived from animal feed, known as saturated fats, the calorie added intake is low in proportion to the proteins consumed.
And what about carbohydrates, what should you take and in what quantities?
You will avoid fast sugars, glucose, or fructose with a high glycaemic index, i.e., requiring a breakdown in the pancreas and liver with insulin. What for? For two reasons, the first is that they create frequent cravings because of the hypoglycaemia that these sugars cause and the signal that is the consequence on the body, and the second reason is because by taking large doses of fast sugars we become refractory to the transformations of the pancreas which no longer plays its role and this naturally leads to an increase in blood sugar levels, sugar that could not be treated with insulin. You then become pre-diabetic and then quickly become type B diabetic. This is a calamity for the heart. A good substitute for quick sugar is sugar from birch bark, xylitol that can be found commercially (Amazon, greenweez) or organic coconut sugar. You can find more on the internet. Starchy foods like potato, pasta, rice are also carbohydrates, they are classified as slow carbohydrates, but they can have a high glycaemic index. To lower this glycaemic index, sweet potatoes should be used instead of normal potatoes, and for rice and pasta, semi-whole or whole grain products that contain fibre should be favoured, or fibre should be added to preparations (whole tomatoes, lettuce, carrots, spinach, mashed leeks, etc.).
Should you add dietary fibers or probiotics?
Fibre and bacteria, probiotics, lactic acid ferments (lacto, Bacillus gasseri for example, found in yoghurts). These elements are often absent from the diet in France and yet, they must be incorporated into the daily diet. They allow you to achieve satiety, so you tend to eat less, and facilitate intestinal transit and digestion, i.e., the transformation of what you eat into assimilable nutrients. Keep in mind, however, that the food you eat is processed to a certain extent in your own flesh and that there is no longer any difference between your body before and after ingestion, like the small hand of the clock that never seems to move forward on the dial. The undigested portion is eliminated through the large intestine. The quality of the food you ingest therefore creates your own excellence.
Are there any natural appetite suppressants?
One fibre is to be noted, glucomannan from a tuber plant, konjac. It is a fiber that absorbs 100 times its weight in water, traps fats and sugars dissolved in water, and it accompanies a diet by increasing its satiating effect and eliminates hollow effects. This product can be found on sale at Amazon or in health food stores as a dietary supplement.
Where should vitamins and minerals be found?
Vitamins of groups B, C, D and especially E (from alpha to gamma the most antioxidant of all) that are found in fruits and vegetables or oils. Minerals such as zinc, magnesium, iron, selenium, copper, iodine, which are found naturally in quantities in meat and fish.
But then, what makes you fat?
What is the relationship between nutrients (proteins, proteins), fats, oils and fats, carbohydrates (sugars) and calories. As far as we are concerned, remember that when you exceed the amount of Kcal you need per day depending mainly on your activities and age, part of it is stored instead of being sent to the large intestine. This part is the carbohydrates that are stored in glycogen and then in fat. It is not fats and oils that make fat, because the excess of these is eliminated by the large intestines, but the culprits are the carbohydrates that contain the fast sugars and the slow or starchy sugars. As soon as your daily calorie consumption is less than the amount ingested and this amount contains carbohydrates (slow or fast), you store the difference. This is when a fattening product is said to be fattening, such as potatoes, pasta, or bread. But it only comes when there's a calorie surplus. It comes from an old habit of your brain, which, fearing to miss out on days of scarcity, stores the excess carbohydrates just in case. So, if you consume fewer calories than you need in a day, you can consume sugary products without gaining weight. Conversely, if you consume more calories than you need but don't consume sugar or starchy foods (slow sugars), you don't gain weight either. Keeping a normal meal, a day helps to better regulate this overflow and therefore avoid weight gain. In addition, any daily deficit has the advantage in this case of destock fat in glycogen and then glucose so that the muscles or brain get their minimum daily intake: usually, you lose weight. Recommend Use a Sanitas scale model SBG21 that provides you with your weight, BMI, useful calories, body fat, bone, and water. Unfortunately, it does not indicate the necessary proteins.
What products do the brain need then?
A distinction must be made between gaseous, liquid, and solid products:
Gaseous products
There are three kinds of gaseous products that influence the brain.
Oxygen: It is an essential element for the proper functioning of the brain, which consumes about 20% of the oxygen we breathe. Is it necessary to remember that when we eat slowly, we take care to breathe, and that when we eat quickly, we lack oxygen during the time of swallowing. So, to nourish your brain at the same time as the food you absorb, you must eat slowly, and also for many other reasons that you can discover on the net. (Salivary Predigesting, Jaw Activation, Palatability Countdown and many more)
Odours and esters:
They are also gases produced by prepared or natural foods. They promote pleasure and appetite for eating. It is therefore important to keep this factor in the diet so as not to fall into boredom when it comes to eating. It is therefore necessary to respect and cultivate the smells and esters produced by the prepared cuisine (think of the smell of grilled prime rib or sausage for example, or the smell of truffles, vanilla which awakens the pleasure of the taste buds and the palate).
Social Sharing Pheromones:
The social effect of shared meals is often overlooked, but the shared pleasures of the table are identical to pheromones produced during sexual acts, but to a lesser extent and without our knowledge. On the other hand, they predispose to the social sharing of food in society and promote good nutrition and digestion.
Liquid products:
The two main ones are:
Water: